A company’s Earnings Before Interest & Taxes (EBIT), also referred to as the Operating Profit, measures residual profits after accounting for the company’s cost of goods sold (COGS) and operating expenses.
The EBIT calculation excludes the interest expense and income taxes in an attempt to measure the core business model. The amount of debt service and income taxes will vary greatly between companies, so a more accurate measure of a core business is to exclude those items and focus only on revenues, cost of goods sold, and operating expenses.
The EBIT calculation is the following:
EBIT = Gross Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses
A company can usually calculate its EBIT by taking its after-tax net income and adding back interest expense and income taxes.
Example EBIT Calculation for Company A
Company A’s income statement shows the following revenue and expenses for the 2023 fiscal year.
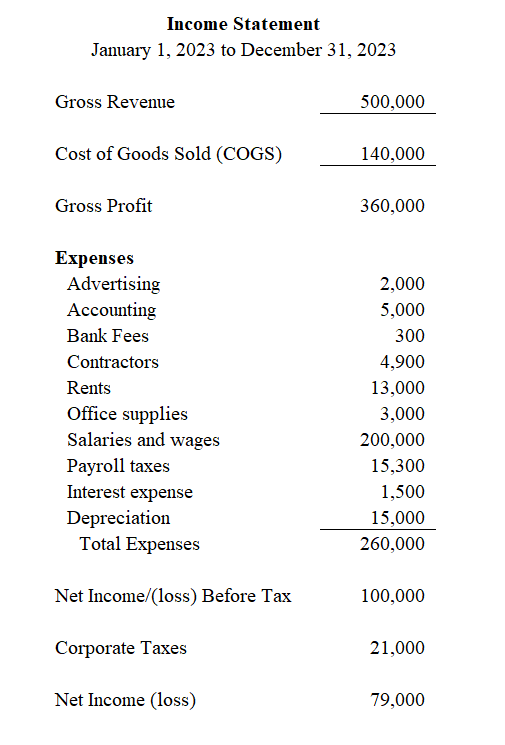
The company calculates its EBIT as follows:
Company A totals its operating expenses, excluding interest expense and corporate income taxes.
Operating Expenses = (2,000 + 5,000 + 300 + 4,900 + 13,000 + 3,000 + 200,000 + 15,300 + 15,000)
Operating Expenses = 258,500
EBIT = $500,000 – $140,000 – $258,500
EBIT = $101,500
The Company’s EBIT is $101,500 for the 2023 fiscal year.
Alternative EBIT Formula
Company A could take its net income and add back interest & depreciation expenses.
EBIT = Net Income + Income Taxes + Interest Expense
EBIT = $79,000 + $21,000 + $1,500
EBIT = $101,500

